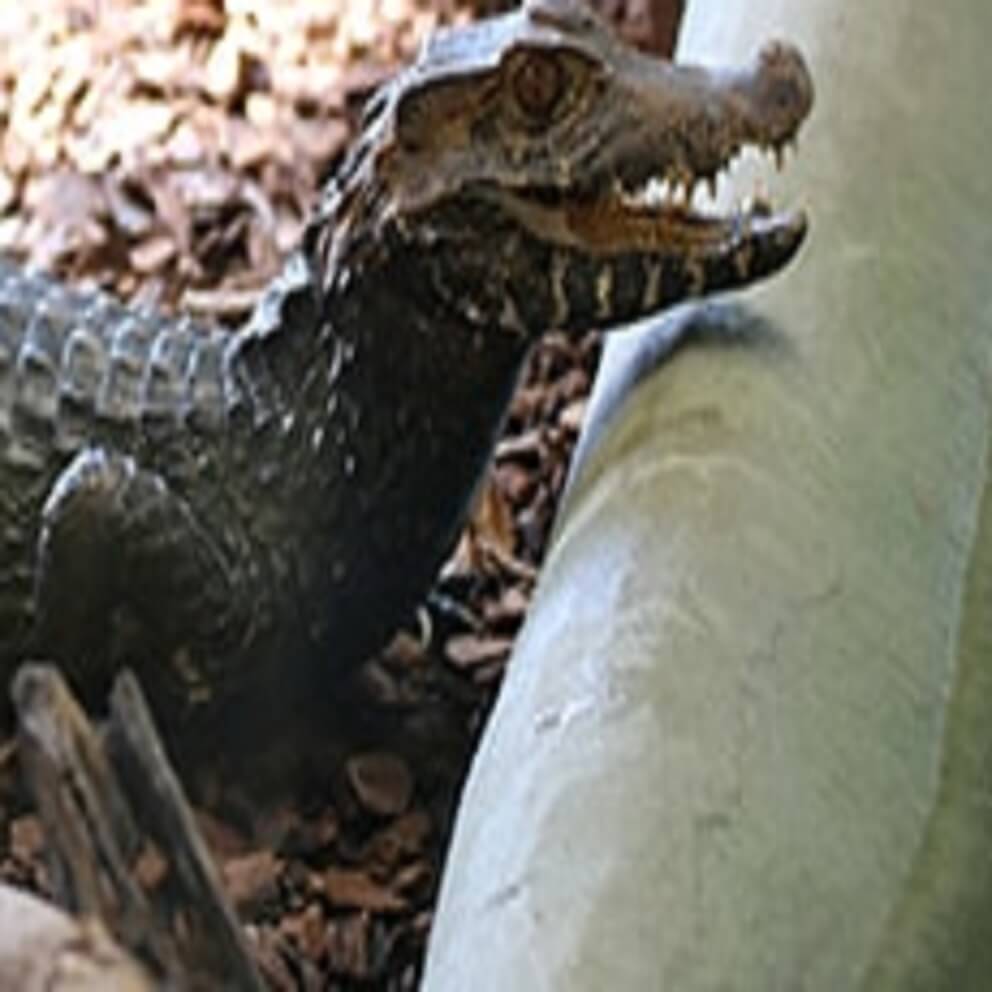
Cuvier’s dwarf caiman is classified as Lower Risk/least concern on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
It is listed on CITES Appendix II.
Red List Category & Criteria: Lower Risk/least concern ver 2.3
Year Published: 1996
Date Assessed: 1996-08-01

Countries: Bolivia; Brazil; Colombia; Ecuador; French Guiana; Guyana; Paraguay; Peru; Suriname; Venezuela; Trinidad & Tobago.
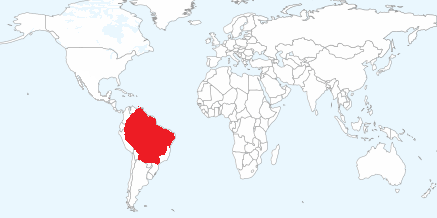
Cuvier’s dwarf caiman is a freshwater species native to tropical northern and central South America. It is found in forested riverine habitats and areas of flooded forest around lakes. It seems to prefer rivers and streams with fast-flowing water but is also found in quiet, nutrient-poor waters. It is able to travel quite large distances overland at night and individuals have sometimes been found in isolated, temporary pools.
Cuvier’s dwarf caiman seems relatively tolerant of cool water compared to other species of crocodile.
Adult Cuvier’s dwarf caiman feed on fish, crabs, shrimps, molluscs, and other invertebrates, along with amphibians and small mammals – both on land and in the water. Juveniles eat fewer fish but also consume crustaceans as well as land invertebrates such as beetles. They have short, backward-curved teeth, which are particularly suited to taking invertebrates and crustaceans.
Threats for Cuvier’s dwarf caiman come from habitat destruction, and pollution (for example, through gold mining activities). As jungle habitat is developed further and roads encroach into these jungles, dwarf caimans are becoming victims of car strikes as they move about at night. Collection for the pet trade is permitted in Guyana, but under strict quotas that are rarely filled. Dam construction can impact dwarf caimans, but the effect can be difficult to quantify (some impacts negative, some positive).
Despite extensive survey data on population status, little was known about the biology and ecology of this species. In recent years, these gaps are beginning to be filled.
Est. wild population: More than 1,000,000
Main conservation threats: Habitat destruction, pollution.



